Digestive health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, yet many individuals neglect or misunderstand the signs that indicate a need for specialized care. Gastrointestinal issues can range from mild discomfort to severe disorders that can significantly impact your quality of life. Understanding when to seek the expertise of a gastroenterologist is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Read on to learn the signs and symptoms that indicate when should you see a gastroenterologist.
Understanding The Role Of A Gastroenterologist
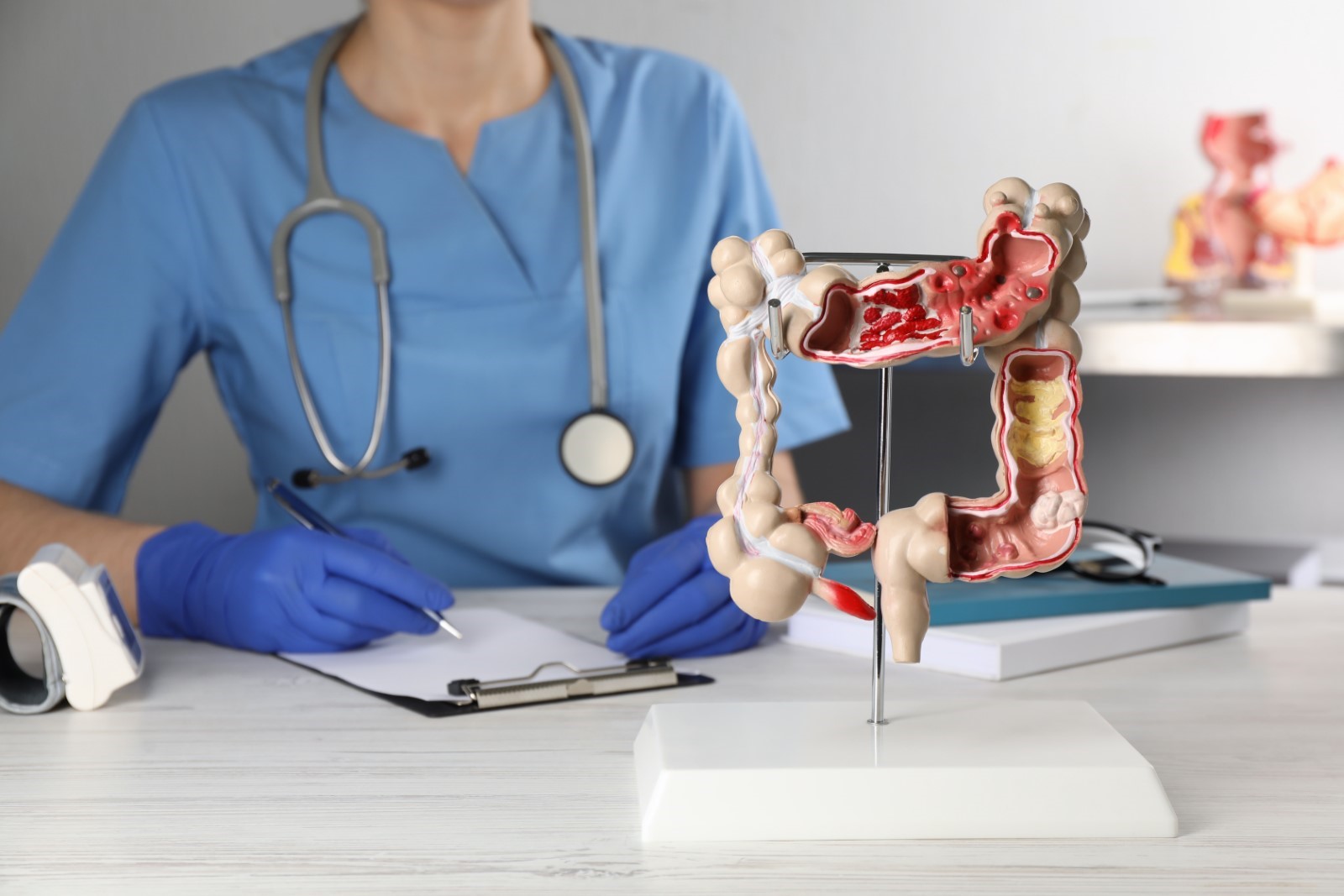
A gastroenterologist is a medical specialist extensively trained in diagnosing and managing disorders of the gastrointestinal (GI) system and liver. Their expertise covers all major components of the digestive system, including:
- Disorders like esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus;
- Conditions such as gastritis and peptic ulcers;
- Issues like celiac disease and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO);
- Diseases such as colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD);
- Problems including hemorrhoids and rectal prolapse;
- Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer;
- Gallstones and biliary duct obstruction;
- Hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Gastroenterologists are proficient in diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, and liver biopsy. These procedures allow them to precisely diagnose conditions, assess the severity of diseases, and implement targeted treatments ranging from medication management to advanced interventional therapies.
Therefore, if you’re experiencing any of the above-mentioned medical conditions, it’s best to consult with an experienced gastroenterologist in your area to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms Requiring A Gastroenterologist’s Care
As mentioned, recognizing when to seek the expertise of a gastroenterologist is crucial for addressing digestive health concerns. Several common symptoms may indicate underlying gastrointestinal issues that require professional evaluation. These include:
Persistent Heartburn And Acid Reflux
Persistent heartburn, characterized by a burning sensation in the chest or throat, when occurring more than twice a week, often points to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This common digestive disorder involves the backflow of stomach acids into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. If left untreated, GERD can evolve into more severe complications such as esophageal ulcers, which are open sores in the esophagus, or Barrett’s esophagus, a condition where the esophageal lining changes, potentially leading to esophageal cancer.
Abdominal Pain And Bloating
Abdominal pain and bloating that persist can be distressing symptoms, indicative of various gastrointestinal conditions. Chronic or intense abdominal discomfort may signal irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms including cramps, bloating, and alterations in bowel habits without any underlying damage to the gut.
Alternatively, these symptoms could also be associated with celiac disease—an autoimmune disorder where gluten ingestion leads to intestinal damage—or even intestinal blockages, which are physical obstructions in the digestive tract.
Changes In Bowel Habits
Noticing significant changes in bowel habits, including persistent diarrhea or constipation, can be alarming and may suggest serious gastrointestinal issues. Conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis—both forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)—lead to chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, manifesting in severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Another concerning possibility is colorectal cancer, which may initially present as changes in bowel habits.
Rectal Bleeding
Rectal bleeding, evident as bright red blood or darker stools should never be overlooked and warrants immediate medical attention. While often caused by relatively benign issues such as hemorrhoids or anal fissures, which are small tears in the lining of the anus, it can also signify more grave conditions like colorectal cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss, particularly when significant and not linked to changes in diet or exercise, can be a concerning symptom of various gastrointestinal disorders. Conditions such as advanced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or gastrointestinal cancers can lead to a drastic reduction in body weight as these diseases often impair nutrient absorption or decrease appetite.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
Difficulty swallowing, or dysphagia, can be a distressing symptom indicating the presence of an esophageal disorder. Conditions such as esophageal strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), achalasia (a disorder impairing the ability of the esophagus to move food toward the stomach), or esophageal cancer can all manifest as dysphagia. These conditions may cause discomfort or even pain during eating, leading to avoidance of food and subsequent weight loss.
Diagnostic Tools and Procedures
Gastroenterologists employ a range of diagnostic tools to effectively identify the root cause of gastrointestinal symptoms. These include:
- Endoscopy: This procedure involves using a flexible tube with a light and camera to view the digestive tract. An upper endoscopy examines the upper digestive system, while a colonoscopy is used to examine the colon.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasounds can help visualize the gastrointestinal tract and surrounding structures, providing valuable information that can’t be obtained through physical examination alone.
- Biopsies: Taking small samples of tissue for analysis can help diagnose conditions like cancer, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Manometry and pH Monitoring: These tests measure the pressure and pH level within the digestive tract, helping to diagnose conditions that affect bowel movements and acid reflux.
With these tests, a gastroenterologist can provide proper diagnosis and treatment for your gastrointestinal condition. Also, it’s advisable to see a gastroenterologist if you experience any of the symptoms or if you have a family history of GI diseases like colorectal cancer. Also, adults over 45 are recommended to undergo routine colonoscopy screenings for colorectal cancer prevention.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms that warrant a visit to a gastroenterologist can lead to earlier detection and treatment of potentially serious gastrointestinal conditions. If you experience any significant changes in your digestive health, don’t hesitate to consult a specialist. Remember, taking timely action can be crucial in maintaining your digestive health and your overall well-being.