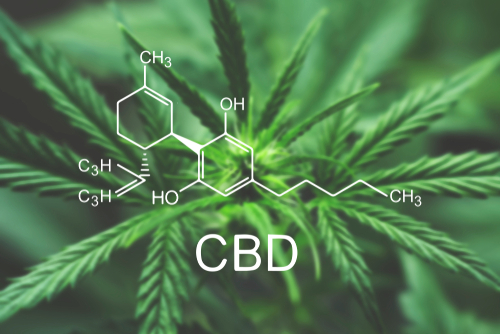
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) has been discovered or identified in the early 1990s. This happened when researchers were studying THC, a cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Currently, the ECS is known for its role in the regulation of a few human and animal functions like sleep, memory, and appetite. Now, even if the ECS is connected to cannabinoids like THC and CBD, this doesn’t mean that it only functions or exists when it is triggered by a cannabinoid from the cannabis plant. The ECS is actually active even without these cannabinoids. The THC and CBD are the two well-known cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. However, what should be emphasized is that these two are not exactly the same. THC or tetrahydrocannabinol can give its user the feeling of euphoria. In other words, it could get a person high. Meanwhile, CBD or cannabidiol alone doesn’t give its users such effects. What’s common between the two is that they are both found to have benefits. CBD is more popular when it comes to medical use. A lot of people are using CBD products like CBD oil for anxiety, depression, and pain management. It is found to have compounds to help a person remain calm and feel less pain. The main function of the ECS is to maintain a body’s homeostasis. Homeostasis is the balance within the body, and this includes the body’s temperature and water and salt concentration. Researchers found that cannabinoids from the cannabis plant can help maintain homeostasis through their interaction with the components of the ECS. The Main Components of the Endocannabinoid System This system found in every human’s body includes three main components. Here’s what you need to know about them.
- Endocannabinoids
The endocannabinoids are natural compounds found in your body. These are also naturally produced by the cannabinoids that come from the cannabis plant. However, even without the use of any cannabinoids like THC and CBD, endocannabinoids are still present in one’s body. So far, there are only two endocannabinoids that are already identified in a human’s body, and they are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol or 2-AG.
- Endocannabinoid Receptors
The endocannabinoid receptors are what signal the whole ECS to function. These are bound by the endocannabinoids in your body. There are also two main receptors identified in a human’s body. The CB1 and CB2 receptors. The CB1 receptors are mainly found in the central nervous system. This means that endocannabinoids that target CB1 receptors are most likely to act on problems that concern the nervous system, like pain in the spinal nerve. Meanwhile, the CB2 receptors are found in the peripheral system of a human’s body. If endocannabinoids target CB2 receptors, it would help fix inflammation or some symptoms of autoimmune disorders.
- Enzymes
The enzymes are responsible for your endocannabinoid metabolism. They are responsible for the degradation of the endocannabinoids in your body. However, they only make sure to do this right after the function of the endocannabinoids are already carried out. Each endocannabinoid in your body has its own enzyme that is responsible for their degradation. For the AEA, the fatty acid amide hydrolase is the enzyme responsible to break it down. Meanwhile, the enzyme that breaks the 2-AG down is the monoacylglycerol acid lipase. How Does CBD Affect the Endocannabinoid System? The effects that CBD has on your ECS is very different from THC’s effects. THC can bind with both AEA and 2-AG. CBD, on the other hand, don’t really bind with them. CBD modifies the ability of these receptors to bind with other cannabinoids like THC. So, this means that CBD can help maximize the effect or benefits of other cannabinoids in your body. There are experts who would say that CBD actually prevents enzymes from quickly degrading endocannabinoids. Doing so would lengthen the effects of these endocannabinoids. Some experts also believe that CBD can still bind with a receptor or more. However, it is possible that these receptors are not yet found or named. So far, more studies and researches are needed to really know how CBD affects the endocannabinoid system. Conclusion What’s known is that CBD alone doesn’t have any negative effects on your brain and body when it interacts with your Endocannabinoid system. Professionals also found that unlike THC, the use of CBD is less likely to become a habit or an addiction. This means that its users wouldn’t really have the feeling that they need to use CBD products to feel better.