Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep. The American Medical Association reports that around 30 million people have this condition even though only six million people are diagnosed with it. It happens when the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open, leading to repeated pauses in breathing that can last from a few seconds to over a minute.
There are two main types of sleep apnea:
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type of sleep apnea and occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway during sleep.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This type of sleep apnea is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles to breathe, rather than a physical blockage of the airway.
Here are some of the most common symptoms of sleep apnea:
- Loud snoring: This is one of the most common symptoms of sleep apnea. It is caused by the vibration of the tissues in the throat as air passes through the narrowed airway.
- Gasping or choking during sleep: People with sleep apnea may experience periods of gasping or choking during sleep as they try to catch their breath.
- Restless sleep or insomnia: Interrupted sleep can cause people with sleep apnea to feel restless during the night or have difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep.
- Daytime fatigue or sleepiness: People with sleep apnea often feel excessively tired or sleepy during the day, even after a full night’s sleep.
- Morning headaches: The disrupted sleep patterns caused by sleep apnea can lead to headaches in the morning.
- Memory and concentration problems: Chronic sleep deprivation can affect cognitive function, leading to memory and concentration problems.
- Irritability and mood swings: People with sleep apnea may experience mood swings, irritability, or depression due to the disruption of their sleep patterns.
Diagnosing sleep apnea involves a combination of clinical evaluation and testing. Here are the steps involved in diagnosing sleep apnea:
Consultation: The first step in diagnosing sleep apnea is to talk to your doctor about your symptoms. Your doctor will ask you questions about your sleep patterns, any symptoms you are experiencing, and any other health conditions you may have.
Physical Exam: Your doctor may conduct a physical exam to check for any physical factors that may be contributing to your symptoms. This may include examining your throat, nose, and mouth for any abnormalities that could be causing the airway to narrow.
Sleep Study: A sleep study, also known as a polysomnogram, is the most common test used to diagnose sleep apnea. This test involves spending a night in a sleep lab, where your breathing, heart rate, brain activity, and other bodily functions are monitored while you sleep.
Home Sleep Test: In some cases, a home sleep test may be used to diagnose sleep apnea. This test involves wearing a portable monitoring device that tracks your breathing and other bodily functions while you sleep in the comfort of your own bed.
Diagnosis: Once the test results are reviewed, your doctor will make a diagnosis based on the severity of your symptoms and the results of your sleep study or home sleep test.
If you are diagnosed with sleep apnea, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan based on the severity of your symptoms and other factors. Treatment options can include lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or quitting smoking, as well as medical interventions, such as using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine to help keep the airway open during sleep.
Sleep apnea can be caused by a variety of factors. Here are some of the most common causes and risk factors of sleep apnea:
- Obesity: People who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing sleep apnea. Excess weight can lead to the narrowing of the airway, making it harder to breathe during sleep.
- Genetics: Sleep apnea can also run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the disorder.
- Age: Sleep apnea becomes more common as people get older, particularly in those over the age of 60.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop sleep apnea, although the risk increases in women after menopause.
- Smoking: Smoking can cause inflammation and narrowing of the airway, increasing the risk of sleep apnea.
- Alcohol and sedatives: Drinking alcohol or taking sedatives can relax the muscles in the throat, making it harder to breathe during sleep.
- Medical conditions: Medical conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and asthma can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Structural abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the nose, mouth, or throat, such as enlarged tonsils, a deviated septum, or a small jaw, can also increase the risk of sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea can have a range of health consequences if left untreated, including an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and depression. People with diabetes need to be especially careful about avoiding complications, which means keeping their sleep issues in check. It is important to talk to your doctor if you are experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea or if you are at risk for the disorder. Treatment options can include lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or quitting smoking, as well as medical interventions, such as using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine to help keep the airway open during sleep.
Treating sleep apnea is important because it can have serious negative impacts on both short-term and long-term health. Here are some reasons why treating sleep apnea is important:
- Improved Quality of Life: Sleep apnea can cause daytime fatigue, reduced cognitive function, and mood changes, which can negatively affect a person’s quality of life. Treating sleep apnea can improve these symptoms and help people feel more rested and alert during the day.
- Reduced Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. Treating sleep apnea can help reduce the risk of these conditions.
- Reduced Risk of Accidents: Sleep apnea can cause daytime sleepiness and impair cognitive function, which can increase the risk of accidents at work or while driving. Treating sleep apnea can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Improved Glucose Control: Sleep apnea has been linked to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Treating sleep apnea can help improve glucose control in people with diabetes.
- Improved Mental Health: Sleep apnea has been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety. Treating sleep apnea can help improve mental health and reduce the risk of these conditions.
Overall, treating sleep apnea is important for improving quality of life and reducing the risk of serious health problems. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have sleep apnea, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
There is evidence to suggest that sleep apnea may be associated with high cholesterol levels. Here are some key findings from studies on sleep apnea and high cholesterol In a study of 110 individuals with untreated sleep apnea, it was found that those with severe sleep apnea had significantly higher total cholesterol levels compared to those with mild or no sleep apnea. A meta-analysis of 17 studies found that individuals with sleep apnea had higher total cholesterol levels, as well as higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (also known as “bad” cholesterol) and triglycerides. In a study of 658 individuals, those with sleep apnea were more likely to have high cholesterol levels compared to those without the condition. Another study of 167 individuals found that those with sleep apnea had higher levels of oxidized LDL cholesterol (a type of LDL cholesterol that is particularly harmful to cardiovascular health) compared to those without sleep apnea. CPAP therapy, the most common treatment for sleep apnea, has been shown to improve lipid levels in some individuals with sleep apnea. For example, a study of 34 individuals with sleep apnea found that CPAP therapy led to a significant reduction in total cholesterol levels after just one week of treatment.
Overall, these studies suggest that sleep apnea may be associated with high cholesterol levels, particularly in individuals with severe sleep apnea. Treatment of sleep apnea with CPAP therapy may help improve lipid levels in some individuals, although further research is needed in this area. It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to have regular cholesterol screenings and work with their healthcare provider to manage their cardiovascular risk factors.
Sleep apnea has been found to be associated with an increased risk of strokes. Here are some key findings from studies on sleep apnea and strokes:
- In a study of over 1,000 individuals, it was found that those with moderate to severe sleep apnea had a higher risk of developing stroke compared to those without sleep apnea.
- Another study of over 1,000 individuals found that those with sleep apnea were more likely to have a history of stroke compared to those without sleep apnea.
- A meta-analysis of 29 studies found that individuals with sleep apnea had a higher risk of both ischemic stroke (caused by a blockage in a blood vessel) and hemorrhagic stroke (caused by bleeding in the brain) compared to those without sleep apnea.
- In a study of 1,022 individuals with sleep apnea, those who received treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy had a significantly lower risk of stroke compared to those who did not receive treatment.
- It is thought that the increased risk of stroke in individuals with sleep apnea may be related to the repeated drops in blood oxygen levels that occur during episodes of apnea, which can lead to changes in blood pressure and a higher risk of blood clots.
Overall, these studies suggest that sleep apnea may be associated with an increased risk of strokes. Treatment of sleep apnea with CPAP therapy may help reduce this risk, although more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between sleep apnea and strokes. It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to work with their healthcare provider to manage their cardiovascular risk factors and reduce their risk of strokes and other related conditions.
There is evidence to suggest that sleep apnea may be associated with an increased risk of depression. Here are some key findings from studies on sleep apnea and depression:
- In a study of over 9,000 individuals, those with sleep apnea were found to have a higher risk of developing depression compared to those without sleep apnea.
- Another study of over 2,000 individuals found that the prevalence of depression was higher in those with sleep apnea compared to those without sleep apnea.
- A meta-analysis of 19 studies found that individuals with sleep apnea had a higher risk of developing depression compared to those without sleep apnea.
- In a study of 1,400 individuals with sleep apnea, those who received treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy had a significant improvement in symptoms of depression compared to those who did not receive treatment.
- It is thought that the increased risk of depression in individuals with sleep apnea may be related to the disrupted sleep patterns and changes in oxygen levels that occur during episodes of apnea.
Overall, these studies suggest that sleep apnea may be associated with an increased risk of depression. Treatment of sleep apnea with CPAP therapy may help improve symptoms of depression, although more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between sleep apnea and depression. It is important for individuals with sleep apnea to work with their healthcare provider to manage their mental health and reduce their risk of depression and other related conditions.
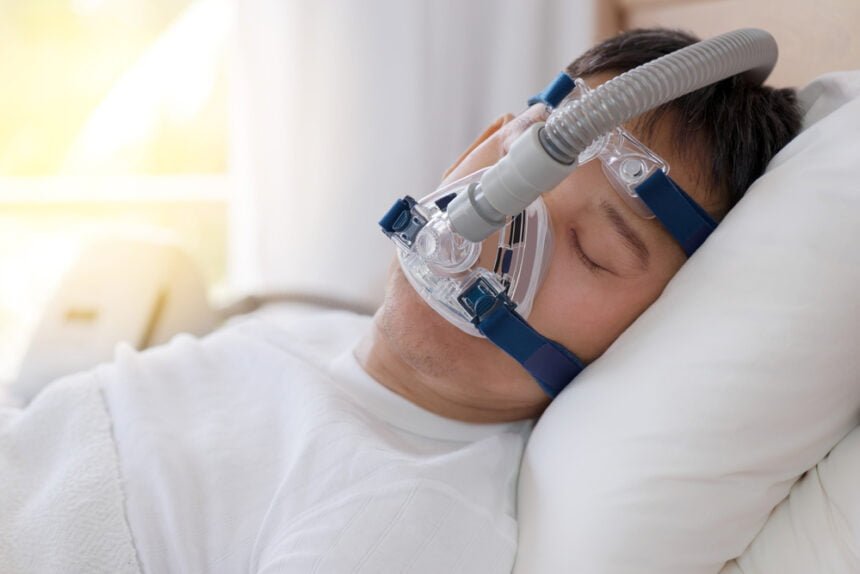
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machine is a common treatment for sleep apnea. A CPAP machine uses a mask worn over the nose or mouth, which is connected to a machine that delivers a continuous stream of air to keep the airway open during sleep.
The CPAP machine works by increasing air pressure in the throat, which helps to prevent the airway from collapsing or becoming blocked during sleep. This keeps the airway open, allowing for normal breathing and reducing the number of apnea or hypopnea events (pauses in breathing) during sleep.
CPAP therapy is often effective in treating sleep apnea and can improve symptoms such as snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, and fatigue. However, it can take some time to adjust to using a CPAP machine, and some people may experience discomfort or difficulty using the device.
It is important to work with a healthcare professional to ensure the correct settings and mask are used for your CPAP therapy. In some cases, other treatments may also be recommended, such as weight loss, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
There have been several advancements in CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) technology in recent years, aimed at improving comfort and ease of use for patients. Here are some examples of new technologies for treating sleep apnea:
- Auto-titrating CPAP: Also known as APAP (automatic positive airway pressure), this type of CPAP machine adjusts the air pressure in real-time based on the patient’s breathing patterns during sleep. This can provide a more customized and comfortable therapy, as the machine can respond to changes in the patient’s breathing.
- Bi-level CPAP: This type of CPAP machine offers two different levels of air pressure during inhalation and exhalation. This can be helpful for patients who have trouble exhaling against the pressure of a traditional CPAP machine.
- Humidification: Many modern CPAP machines include built-in humidifiers, which can help to prevent dryness or irritation in the nose and throat that may be caused by the continuous flow of air. This can improve comfort and compliance with CPAP therapy.
- Mask technology: There have been several advancements in mask design and materials, aimed at improving comfort and reducing leaks. For example, some masks now feature gel cushions, adjustable headgear, and more lightweight and breathable materials.
- Mobile connectivity: Some CPAP machines now offer mobile connectivity, allowing patients to track their therapy progress and adjust settings using a smartphone app or other device. This can provide greater flexibility and convenience for patients.
These new technologies for CPAP machines can help to improve the effectiveness and comfort of CPAP therapy and may help to increase patient compliance with treatment.