Waste from the healthcare industry is a major problem across the globe, as the industry is major contributor of the landfill waste. The Practice Greenhealth Sustainability Benchmark Report published in 2015 stated that an average medical waste generated by operating room is more than 5.4 tons per year, which costs around USD 5,243 to the operating room. The problem got worse due to manufacturing of “single-use” clinical instruments and supplies on the backdrop of rising concerns about patient safety, convenience and cost of product. As single-use devices such as surgical scissors, As single-use devices such as surgical scissors, surgical headlights, ultrasound catheters, drills, and other accessories ultrasound catheters, drills, and other accessories are designed to be used once and tossed, creating huge amount of medical waste. Enter the reprocessed medical devices industry. According to report by Grand View Research, Inc., the global medical waste management market size was valued at USD 21.0 billion in 2016 and is expected to grow with CAGR of 5.4% over the forecast period.
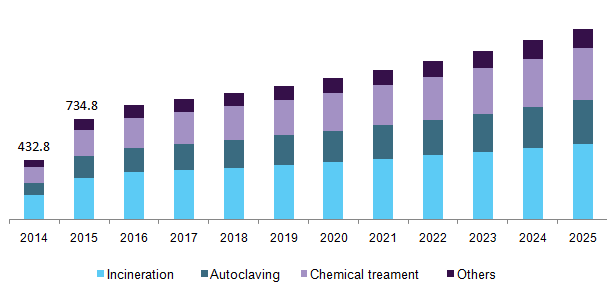
China Medical Waste Management Market, By Treatment, 2014-2025 (USD Million)
What is medical devices reprocessing?
Reprocessing is regarded as the cleaning, disinfecting, sterilizing, reconditioning, repairing and refurbishing of medical devices. There are three types of reprocessing: in-house reprocessing, third-party reprocessing and non-compliant reprocessing. Third-party preprocessor. Market is shifting towards third-party reprocessor as rising number of collaborations of hospitals with third party reprocessors. Grand View Research, Inc. quoted that the global reprocessed medical devices market was estimated at USD 1.64 billion in 2016 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 20.6% over the forecast period. Rising clinical urgency to reduce the generation of medical waste in hospitals and other healthcare settings is a significant growth driver of the market.
Global Reprocessed Medical Devices Market, By Product, 2012-2022 (USD Million)
Single-use devices (SUDs) or disposable devices reprocessing:
In the 1980s medical devices manufacturers discovered a problem in the marketing of their devices, as their devices were too good and they were used by hospitals again and again. Thus, manufacturers started labeling their devices as “single-use” to reduce the rate of reuse of product and to increase company’s revenue. The trend of manufacturing single-use medical devices and accessories paralleled by another trend of cleaning and reusing these devices for another patients, but the practice was carrying significant risk in it and FDA started regulating the reprocessed medical devices market since 2000. FDA has allowed reuse of 70 medical devices that are divided in to three categories based on risk factor of the device[4]. The high-risk devices such as implanted infusion pumps, balloon angioplasty catheters are reprocessed only if sufficient evidence of safety, effectiveness has been recorded and reprocessing facility has been inspected. For medium-risk devices such as laparoscopic instruments, ultrasound catheter, which require safety evidences but no need of inspection; while, low-risk medical devices such as tourniquet cuffs, elastic bandages can be reprocessed without submission of efficacy or safety data.
Reusable devices reprocessing:
Reusable medical devices are the devices that can be used on multiple patients, such as stethoscopes, endoscopes, surgical forceps, etc. The devices are grouped into three types based on their critical level. Non-critical devices, which are in contact with unbroken skin such as stethoscopes; semi critical devices that come in to contact with mucus membrane, which includes duodenoscopes, bronchoscopes, endoscopes; and critical devices that are operated in contact with blood and tissue, such as surgical staples, clamps, forceps. In-house reprocessing is widely preferred for reusable devices as it is a more economic option. Rising clinical urgency to reduce the medical waste generation in hospitals and other healthcare settings, reprocessing methodological advancements are anticipated to present industry growth in immediate future.
Regulatory landscape:
The reprocessing of medical devices for surgical procedures is one of the key factors of quality assurance in healthcare facilities. Any deficiency in the implementation of reprocessing measure could result in hospital-acquired infection (HAI). According to the Multistate Point-Prevalence Survey of Health Care-Associated Infections, in 2014 around one out of 25 patients in the U.S. was detected with HAI. While, a report published by Pharmacoeconomics & Outcomes Research estimates that, in 2018, approximately 2 million patients in the U.S. are estimated to be infected with HAI of which an estimated 90,000 patients will die. Market study conducted by Grand View Research, Inc., states that the global hospital acquired infections (HAI) diagnostics market size was estimated to be USD 3.6 billion in 2015. The report further states that the HAIs have been of increasing concern in healthcare facilities across the globe. According to the WHO, among hundred patients in hospitals, ten patients are estimated to suffer from HAIs in developing countries, and seven in developed countries. On the backdrop of rising HAI incidences, medical devices regulating bodies initiated regularization of reprocessed medical devices.
Asia Pacific HAI Diagnostics Market, By Country, 2012-2022, (USD Million)
- The U.S. FDA was first to regulate the reprocessed medical devices industry. FDA regulated the SUDs reprocessing procedures, all the reprocessors in the industry including hospitals, OEMs and third-party reprocessors.
- Since 2001, Germany had a regulatory framework, and The German Medical Devices Law and the Medical Devices Operator Ordinance regulates the reprocessing of medical devices. The guidelines that do not distinguish between “reusable” and “single-use” devices and allows for reprocessing of all SUDs if standards are met.
- However, other members of European Unions, including France, Spain, and UK prohibited SUDs reprocessing.
- In 2003, Australia enacted regulations for Reprocessing of SUDs. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates the requirements of all reprocessors.
- The reuse of SUDs is found to be more common in Asia, as there are no national regulations to govern the reuse of SUDs.
Thus, favorable government initiatives to promote awareness pertaining to the reprocessing of medical devices are expected to provide this market with significant growth opportunities. Moreover, the presence of stringent regulatory framework in order to ensure patient safety is expected to widen the base for high quality reprocessed devices, therefore generating potential future growth prospects.
Reprocessed Medical Devices: Adoption Trend
Future growth:
The adoption of reprocessed medical devices in healthcare facilities is rising. It is attributed to the need for affordable medical device alternatives. Moreover, reprocessed medical devices are as effective as new devices, which help in cost saving to hospitals and other healthcare establishments. Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson) and Intermountain Healthcare entered into partnership to tackle the issue of medical waste. The companies adopted circular system approach to reduce operating room expenses and reduce medical waste. In 2015, the approach saved around 22% on total spending of medical devices manufacturing. Also, the company diverted 59,964 pounds of waste from landfills. Thus, ongoing efforts by key companies in the medical devices market to manufacture reprocessed medical devices, use of new technologies for reprocessing methods will further boost uptake of reprocessed medical devices in near future. In addition, prices of reprocessed medical devices are almost half of the original equipment, which makes them reasonable for procurement, thereby boosting demand. The data published by Practice Greenhealth in 2013, shows that new ultrasound catheter costs about USD 2,900 while a reprocessed one costs USD 1,400. Similarly, the original laparoscopic device can cost USD 1,240, but a refurbished one costs USD 250. The following table shows the difference between original and reprocessed medical device cost.
Conclusion:
The increasing pressure on healthcare facilities for the proper disposal of medical waste and rising awareness pertinent to it are the factors contributing towards increased adoption of reprocessed medical devices. Similarly, the initiatives taken by the government& private groups, to endorse the use of reprocessed medical devices are the high impact rendering drivers for the industry.