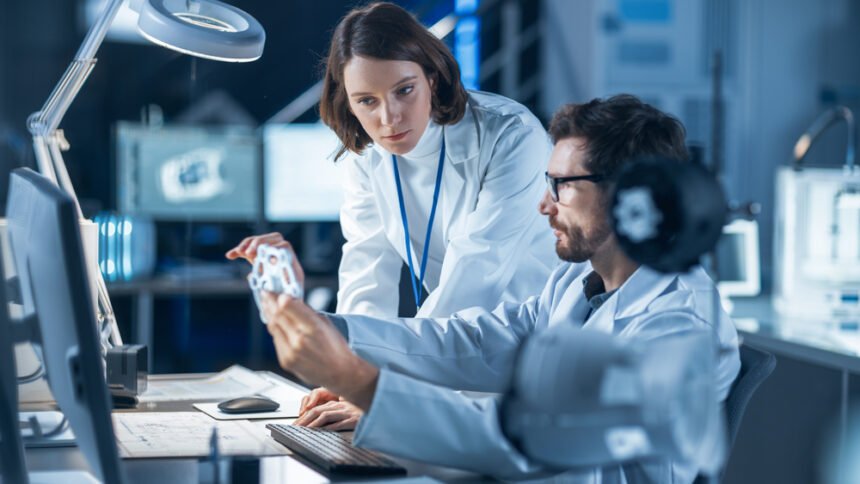
Innovations and advancements in precision machining have made CNC machining and rapid prototyping essential methods in the production of life-saving medical devices. The multi-axis CNC machining technic can answer the requirement for precision, repeatability, and consistency in the medical industry.
The use of prototyping gives doctors, designers, and patients an innovative road for creating a physical representation of the desired design to test its usability quickly. The produced medical devices and models find an indispensable application in many areas in the industry, from planning treatment for complex surgery procedures, surgical simulation, and training, to diagnosis, and design, and production of implants and medical tools.
With that in mind, let us see the most common prototyping methods this industry uses and the most prevalent medical models that can be produced.
CNC Machining and Rapid Prototyping: Which is Better?
Parts and components processed for the medical industry usually require high accuracy, quality, and consistency. What is more, they must also be durable, and with a smooth finish. So in this respect, CNC machining is the best method to achieve and satisfy all the industry requirements, simply because these machines operate on multiple axes. As a subtractive manufacturing process, with CNC machining, a solid piece of raw material is carved into a desired 3D geometrical shape through the use of a controlled material removal process. This process relies heavily upon the use of machine tools in addition to power and hand tools. CNC machining allows for precision part replication and consistency in even the most intricate designs, surfaces, and versatile materials, which makes the CNC parts it machined with better features.
Rapid prototyping (RP) is another technique commonly used in the medical industry to create working prototypes from 3D models. Product designers apply RP, especially in the early design stages, to generate relevant feedback for the design team, decrease development time and costs, encourage potential product enhancements, and foster better customer satisfaction. This method of production allows for extreme flexibility in the design and cost-effective production of complex parts. The RP process is considered more efficient (than CNC machining) in both time and labor, but the material selection is still limited. Furthermore, this method of production is highly accessible, so nowadays you don’t have to invest in your own equipment to start a project. Rapid prototyping is now available online, and you can order the prototypes or custom items you need in an instant.
Even though rapid prototyping is often considered only as a 3D printing application (which is an additive process), manufacturing methods that rely on CNC-controlled machines are also part of this technology. So, as the advancement of innovations swiftly improves both techniques, in time, they come closer and closer in capabilities and performance, which makes the selection process increasingly difficult. Therefore, it is best to combine their strengths – where possible, to get the best value out of the process.
Spheres in the Medical Industry Where Prototyping Plays an Essential Role
Manufacturing Medical Devices
Prototyping technology is used both in the designing and manufacturing of medical devices. Additive technologies are especially prevalent when the devices need to be specifically individualized for a particular patient. However, the industry uses RP not just in manufacturing customized devices. From a simple product like a scalpel to surgical fasteners, retractors, and even more complex ones like a heart rate monitor, all can be produced using this technique. And it is so because rapid prototyping allows us to change the design, movement, and add new functions to improve the product’s efficiency without compromising its precision. Using virtual simulation, we can predict even minor errors in the medical devices in the early stage of the product development and amend them before using the model or device on a real person.
What’s more, the future of medical instruments prototyping includes an interactive designing mechanism. With the rise of augmented reality, experts can virtually interact with the equipment to see how it performs in real-life situations, experiencing the product’s size, shape, and dimension in a real-world environment and making changes simultaneously.
Creating Dental Implants
When it comes to dentistry, rapid prototyping is widely used to develop precise dental implants, dental aligners, or tooth crowns that fit each particular patient individually. With the help of the new 3D imaging technologies, dentists can provide an accurate picture of the patient’s treatment plan. However, when it comes to the production of these dental products, CNC machines are the best bet. The reason is that CNC can be programmed to get the exact product dimensions that will perfectly fit a patient with minimal discomfort. What is also interesting is the fact that prototyping can also be used to understand the deformities in teeth, re-positioning, or abnormal growth, which can further help the dental surgeon to identify the exact issue and work on it in the best possible way.
Prosthetics and Implants
Rapid prototyping is also used by orthopedics to create a replica of bone damage, dislocations, and repairing progress. The additive prototyping approach is perfect for creating 3D models of human organs to find the exact complexion and the right surgical procedure. Before RP, prosthetics were designed using the standard measurements of damaged organs. However, that took a significant amount of time to create the final prosthetic, and any small error could lead to redesigning from scratch. Since the introduction of the medical prototyping, designing prosthetics has become much faster with little to no errors. Doctors can take the perfect measurement of the damaged part of the body, and 3D printers can process it to create the prosthetics with the exact size and dimensions. For example, patients whose requirements are outside the standard scope or those who require unique treatments can now get customized prostheses that fit them at an affordable cost. Importantly, as we already mentioned, rapid prototyping allows for changes to the prototype easily. Doctors are in a position to create the final prosthetic that fits the size, dimensions, and color that looks like the exact body organ. Whether it is cosmetic or surgical implantation, rapid prototyping has made it much cheaper, more comfortable, and reliable. For example, a standard method used for medical purposes is the CT scan used in the hip replacement surgical procedure. Here, data from the CT scan is combined with engineering data to join to the bone. Through the use of CNC machining, the data is turned into a plastic model (implant) that fits perfectly and lasts longer for the patient.
Medicines
In the medical industry, prototyping is frequently used to determine the size, shape, dosage form of pills, and their chemical compositions. It is also the best method to predict the potency of the medicine and its effect on a human body before mass manufacturing. Furthermore, the new technology has improved the safety of drugs to patients by minimizing the adverse drug reactions that may arise.
Final Thoughts
When designing a new medical device, the initial idea often goes through several iterations during the design and development process to get to the final design. Consequently, the final design can be significantly different from the original sketched-out idea. For this reason, prototyping is crucial to achieving a final design that is functional, practical, cost-effective, and adheres to regulations. What is important is that medical prototypes are helping medical practitioners be of better service to patients without the long turn over or risks in experimentation.