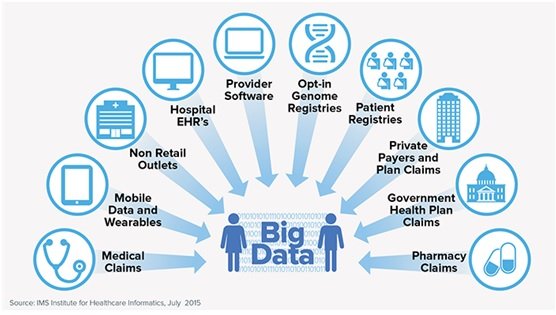
Healthcare stakeholders now have access to promising new areas of knowledge. This information is in the form of “Big data”, so called not by its sheer magnitude but for its complexity, diversity and timeliness which traditional data processing application software are unable to deal with. Pharmaceutical industry experts and providers are looking for new ways to leverage Big data to obtain insights about problems related to healthcare quality and rising healthcare expenses. It is leading to health innovations, like precision medicine, predictive analytics, and machine learning.
A 2011 McKinsey report estimated that the health care industry could potentially realize $300 billion in annual value by leveraging big data.
Why Big Data is needed in healthcare
1) Rising costs of Healthcare
The demand for big data in healthcare is growing, due to rising costs in nations like the United States. As a McKinsey report states, “After more than 20 years of steady increases, healthcare expenses now account for 17.6 percent of GDP —nearly $600 billion more than the expected benchmark for a nation of the United States’s size and wealth.”
2) Insurance company incentive structure is changing – Many insurance companies are swapping from fee-for-service plans to value based, patient centric care. The former rewarded expensive, unnecessary treatments and involved treating large numbers of patients quickly. The focus has moved to patient outcomes now.
Today, healthcare providers are benefitted when they share patient information with one another.
3) Physician decision is becoming more evidence based – Today physicians rely more on large chunks of research and clinical data than their professional opinion. Data collection and management is becoming bigger in healthcare industry, and so professionals need help.
Challenges for implementing Big data
The following section identifies some of the top challenges organizations face when implementing big data and probable solutions to these issues.
CAPTURE
Challenge–The data that healthcare providers get from various sources is not always complete, clean and accurate or formatted correctly to be used in multiple systems.
Poor understanding of merits of big data for data capture,can all lead to quality issues.
Solution– In order to improve their data capture methods, providers have to identify important data types for their projects. Clinical documentation improvement programs have to be developed, that will coach clinicians and other healthcare professionals,so as to ensure that data is useful for further analysis.
CLEANING
Challenge – Healthcare providers are generally unaware of how vital it is to cleanse their data. Incorrect data can damage a big data analytics project, especially when bringing together disparate data sources holding clinical or operational data in different formats.
Solution – Data cleaning ensures that data is accurate, correct, consistent and relevant.
STORAGE
Challenge– Junior clinicians rarely think about where their data is being stored. But this is an important cost, security, and performance issue for the IT department. With rising volumes of healthcare data, some providers are not able to manage the costs and impacts of keeping data centers in their premises.
Solution – Cloud storage has become apopular and reliable option, as costs continue to drop.Accordigng to a 2016 survey, close to 90% of healthcare organizations are using some sort of cloud-based solutions.
SECURITY
Challenge – Data security is the topmost priority for healthcare organizationsand has to be protected against data breaches, hackings and ransomware episodes.
Though there are various guidelines set up by The HIPAA Security Rule for storing protected health information (PHI), data can still becompromised by staff members, who want convenience and avoid lengthy software updates.
Solution –Healthcare organizations must make their staff members aware of the critical nature of data security protocols and consistently review who has access to critical data assets to prevent possible data breaches.
STEWARDSHIP
Challenge – Healthcare data, has a long shelf life. By rule,any patient data should be accessible for at least six years. Data may also be reused or reexamined for purposes such as quality measurement, research or performance benchmarking.
Solution– All healthcare organizations should appoint a data steward to monitor the sensitive data. A data steward can ensure that all elements have standard definitions and formats, are documented properly from creation to deletion, and remain useful for different tasks.
QUERYING
Challenge–Data has to be queried for purpose of reporting and analytics to generate a complete picture of an organization’s status or an individual patient’s health.
The challenge is to overcome complex data and interoperability problems that prevent query tools from accessing the organization’s entire repository of information. This is because data is held in multiple systems and multiple formats and the underlying data may lack standardization and quality.
Solution –Structured Query Language (SQL) can be used to query large datasets and relational databases.
REPORTING
Challenge – Following the query process, providers must generate a report that is clear, to the point, and accessible to the target audience.
Poor data will produce suspect reports, which is bad for clinicians who want to use the information to treat patients.
Solution – A major part of reporting in the healthcare industry is external.Regulatory and quality assessment programs frequently require large volumes of data to feed into quality measures and reimbursement models. To meet these requirements, providers can include qualified registries, reporting tools built into their electronic health records, and web portals hosted by CMS and other groups.
VISUALIZATION
Challenge– When the data is clean and engaging,it is much easier for a clinician to interpret and use it. Complex flowcharts, cramped or overlapping text, and low-quality graphics can lead to misinterpretation of data.
Solution –Organizations should use good data presentation techniques like, charts,correct labeling and color-coding of information to reduce errors.
Some examples of data visualization techniques include heat maps, bar charts, pie charts, scatter plots, and histograms.
UPDATING
Challenge – Healthcare data is not static. It require frequent updates to remain current and relevant. Certain data like patient vital signs may require updates every few seconds. Others such a home address or marital status, require few changes during an individual’s entire lifetime.
Healthcare app challenge for organizations to understand the volatility of big data, how often and to what degree it changes.
Solution – Providers should know which records can be manually updated, which can be automated, how to complete this process without downtime for end-users, and to ensure that updates can be conducted without damaging the quality or integrity of the records. Duplication of data should be avoided.
SHARING
Challenge – Very few patients receive all treatments atone location. In such case sharing of data with with external partners is essential.
When electronic health records are designed and implemented in different ways, it can severely limit the way data is transferred between different organizations. This can leave clinicians weary and without information that they need to make key decisions.
Solution– Developers can use emerging tools and strategies such as FHIR and public APIs, also do partnerships with Common Well and Care quality to share data easily and securely.
Use cases of Big data
1) Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHR is the most widespread application of big data in healthcare. Every patient’s record is kept in a digital record, which includes demographics, medical history, allergies, laboratory test results etc. Both public and private healthcare providers have access to such data via secure information systems. Every record contains a modifiable file, which the doctors can change over time with no paperwork and danger of data replication.
EHRs can give warnings and reminders to patients about when they should get a lab test done or whether they are following the doctor’s orders properly.
2) Predictive Analytics in Healthcare
Predictive analytics is one of the major business intelligence trends which has found its application in healthcare as well.It helps doctors make quick decisions and act upon accordingly. This is very useful in case of patients with complex medical histories, suffering from multiple disorders.
For this, predictive modeling derives data from EHRs.
3) Telemedicine
Telemedicine is present in the healthcare domain since last 40 years, but only today we have been able to implement it successfully, with the help of online video conferences, smartphones, wireless devices, and wearables. Telimedicine refers to delivery of remote clinical services using technology.
It is used to primary consult and diagnose, remotely monitor patients and educate health professionals.
It also provides personalized treatment plans to patients ,and prevent hospitalization or re-admission.
4) Medicine based on evidence– Most hospitals follow a practice, where after a patient is admitted, the doctor some kind of tests in order to identify the cause for symptoms repeatedly. Using evidence-based medicine, the doctor can match symptoms to a larger patient database in order to come to an accurate conclusion more efficiently. Big data plays collects information from different sources and stabilizes it, so one record that describes “high blood pressure” would map to another that describes “elevated blood pressure.”
The rate of error is reduced significantly, by analyzing the patient’s records with all medications prescribed, and monitoring anything that seems out of place.
5) Reduction of Hospital Readmissions–The patients who are at-risk can be identified through big data analytics, based on patient’s past history, patient trends etc. Hospitals can use this to provide necessary care and reduce readmission rates.
6) Value-Based, Patient-Centric Care
The focus on value-based care corresponds with an increased focus on patient-centric care rather than fee-for-service way of care. Big data is helping to personalize care that is efficient and price conscious, transparent in its delivery and billing, and measured based on patient satisfaction.
7) Reduction in Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
According to one study, the healthcare industry is 200% more likely to experience a data breach than other industries, simply because the personal data is so valuable.
Big data can help identifying fraud through its ability to store and go back in history to analyze large unstructured datasets of historical claims and use machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and patterns.This will not only prevent fraud and security threats but also lead to cost reduction.
8) Real-time Patient monitoring
Healthcare facilities are focusing on more proactive care to their patients by constantly monitoring patient vital signs. Real time analysis of data helps sending alerts to care providers who come to know instantly about changes in a patient’s condition.
For example wearable devices are being used for remote or in-home monitoring of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Some companies who are using Big data:
Explorys
Explorys is a company that leverages big data to provide tools for clinical support, at-risk patient population management and cost of care measurement.
It has one of the world’s biggest healthcare databases. They have created applications that can tap into more than 100 billion data points in their database. Their solutions help clinicians analyze multitude of data from different sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and payer financial data, in real time.
Explorys’s analytics tools help mine data and pinpoint the variations among patients and treatments that influence health outcomes. Based on these insights,providers can determine more accurate treatment plans for individual patients or patient populations.
Propeller Health (formerly Asthmapolis)
Propeller Health is a company dedicated to asthma management, focusing on the prevention side rather than the treatment side. It uses sensors for asthma inhalers, along with healthcare mobile app development. The providers can identify at-risk asthma patients before an attack occurs. Their sensors record date and time of use, and pair with GPS-enabled devices like smartphones to track location data.
It also collects weather data, air quality data, and is working towards EHR integration.
Conclusion
Big data helps to capture and bring together all information about a patient and gives a comprehensive view. This can be used for care coordination and outcomes-based reimbursement, population health management, and patient engagement.By gaining a 360-degree view of the patient ,redundant and expensive testing can be eliminated, errors in administering and prescribing drugs can be reduced, and even prevent deaths.