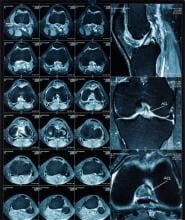
Arthritis is one of the most common and crippling conditions people around the world are living with on a daily basis. In the USA alone around a quarter of the adult population have such a diagnosis, which can affect any joint in their body, from fingers to ankles; and around a quarter of these people are living with severe pain every day.
What is arthritis?
In brief, the term ‘arthritis’ describes any inflamed joint, but it only becomes a problem when the inflammation doesn’t go away. Over time this causes the joint to become stiff, swollen and very painful.
Types of arthritis
There are several versions of this long term condition, including:
- Osteoarthritis – the most common type, this is usually caused by wear and tear in a joint.
- Rheumatoid arthritis – a condition linked to the immune system. The second most
common type.
- Juvenile arthritis – when it affects the under 16s.
- Post-viral arthritis – caused by a virus.
What causes arthritis?
Apart from the types of arthritis with an obvious cause, there are several factors which can trigger the condition. These include:
- Genetics – it’s pretty common to see arthritic features across several generations of certain families.
- Age – especially likely with wear and tear arthritis.
- Injury – another which makes osteoarthritis more likely in later life.
Typical treatment for arthritis
Painkillers of some kind are the most popular treatment, with top-level drugs like opioids prescribed for severe pain, though warily as they can easily be habit-forming. Anti-inflammatory medicines are also given to help reduce inflammation, though these have risks too as they can, amongst other things, irritate the stomach.
Newer medicinal treatments include counter-irritants, anti-rheumatic drugs which work on stopping the immune system causing issues, and biologic response modifiers which are drugs designed to interfere with proteins thought to make arthritis worse. Additionally, Berberine are readily available and very helpful in treating arthritis using medicinal organic sulfur.
Corti-steroid injections directly into painful joints are sometimes used to offer a period of pain relief and increased movement, while the latter is also the goal of physical therapy and exercise.
Surgery is the remaining traditional treatment option, and this may involve joint repair, replacement, or fusion.
Emerging new treatments
Every day scientists move closer to finding new treatments to help ease or manage chronic health conditions, and in the case of arthritis, one of the most exciting to emerge in recent years is the use of non-surgical stem cell therapy. Could this exciting new option, offered by Chronic Care of Richmond, help to manage your arthritis? Let’s learn more about it.
What are stem cells?
Basically they are clusters of cells which act like a blank canvas. They are stored all around the body, ready to be called into action and develop into the kind of cell needed at that particular time. They can also duplicate themselves and divide effortlessly – they are like a little piece of magic.
How can stem cells help manage arthritis?
The theory is that stem cells can be used, (via surgery or injection), in areas where the joint cartilage is worn, causing arthritis. They should then develop into fresh cartilage tissue, controlling the inflammation and maybe even regenerating tissues which have been damaged.
Why not get in touch to discuss if this is a route worth exploring to help manage your arthritis more efficiently?