Accountable Care Organizations, otherwise referred to as ACOs, are transforming the way in which our healthcare system operates. Considered vital components of the healthcare revolution, the main focus of these types of organizations is to emphasize coordinated, quality care for Medicare patients.
Accountable Care Organizations, otherwise referred to as ACOs, are transforming the way in which our healthcare system operates. Considered vital components of the healthcare revolution, the main focus of these types of organizations is to emphasize coordinated, quality care for Medicare patients.
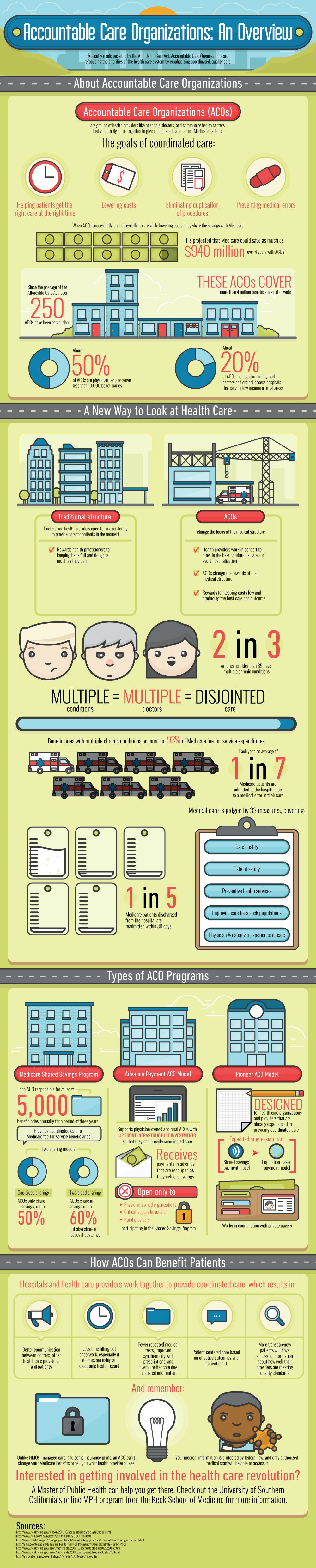
This infographic about ACOs identifies four main goals of the roughly 250 coordinated care facilities established since the passing of the Affordable Care Act:
-
Help patients get the appropriate care in a timely manner
-
Lower overall costs
-
Eliminate unnecessary duplication of procedures
-
Prevent medical errors
As a result of overall lower costs, accountable care organizations can actually share in the savings they create with Medicare, and it’s projected that Medicare could save as much as $940 million over the course of four years.
There are currently three types of ACO programs in existence today:
-
Medicare Shared Savings Programs: These programs are responsible for at least 5,000 beneficiaries annually during a three-year timeframe and provide coordinated care for Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries.
-
Advance Payment ACO Model: This particular model supports physician-owned and rural ACOs with up-front infrastructure investments so that they can provide coordinated care. Payments are received in advance and paid back as the organization’s savings accrue.
- Pioneer ACO Model: These are designed for healthcare organizations and providers that have already adopted the ways of coordinated care.
Source: University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine