Products for the advanced securement of wounds — stopping bleeding, sealing the wound, tightly closing the wound and preventing post-surgical adhesions — will be accepted by clinicians (and paid for by healthcare systems) to the extent that they provide very specific clinical utility compared to traditional alternatives, many of which (like sutures and tapes) are simple to use, cost little and otherwise are readily accepted in the business of wound management.
Products for the advanced securement of wounds — stopping bleeding, sealing the wound, tightly closing the wound and preventing post-surgical adhesions — will be accepted by clinicians (and paid for by healthcare systems) to the extent that they provide very specific clinical utility compared to traditional alternatives, many of which (like sutures and tapes) are simple to use, cost little and otherwise are readily accepted in the business of wound management.
Clinicians (and healthcare systems) will accept and adopt for routine use those new products for hemostasis, closure, sealing and anti-adhesion of wounds, whether chronic or acute, based on the level of clinical utility they provide compared to those traditional products, and the extent to which those new products provide utility is based on the types of utility provided (from “critical” to “perceived”), a metric that varies by clinical specialty. For example, a new product that prevents bleeding and dramatically reduces morbidity is much more likely to be adopted than a product that yields merely aesthetic (e.g., reduced scarring) or perceived benefits that have no impact on morbidity.
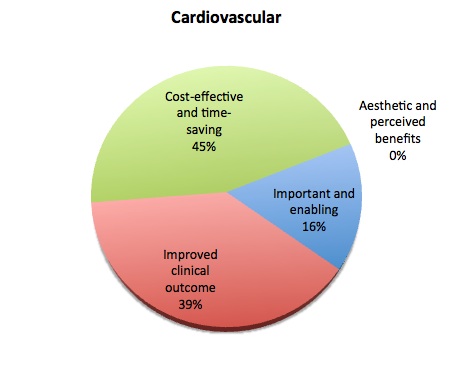
Levels of utility vary by clinical specialty with product usage in many cardiovascular procedures obviously having greater impact than in cosmetic procedures. These include:
- Important and Enabling: Important to prevent excessive bleeding and transfusion, to ensure safe procedure, and to avoid mortality and to avoid complications associated with excessive bleeding and loss of blood.
- Improved Clinical Outcome: Reduces morbidity due to improved procedure, reduced surgery time, and prevention of complications such as fibrosis, post-surgical adhesion formation, and infection (includes adjunct to minimally invasive surgery).
- Cost-Effective and Time-Saving: Immediate reduction in surgical treatment time and follow-up treatments.
- Aesthetic and Perceived Benefits: Selection is driven by aesthetic and perceived benefits, resulting in one product being favored over a number of medically equivalent treatments.
Below is illustrated the distribution — by clinical category — of the kind of utility provided by advanced wound securement products (fibrin and other sealants, high strength adhesives, hemostatic products and anti-adhesion products):
Total: 51.4 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.
Total: 12.7 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.
Total: 20.9 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.
Total: 27.4 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.
Total: 16 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.
Total: 10.8 million procedures
Source: MedMarket Diligence, LLC; Report #S190.